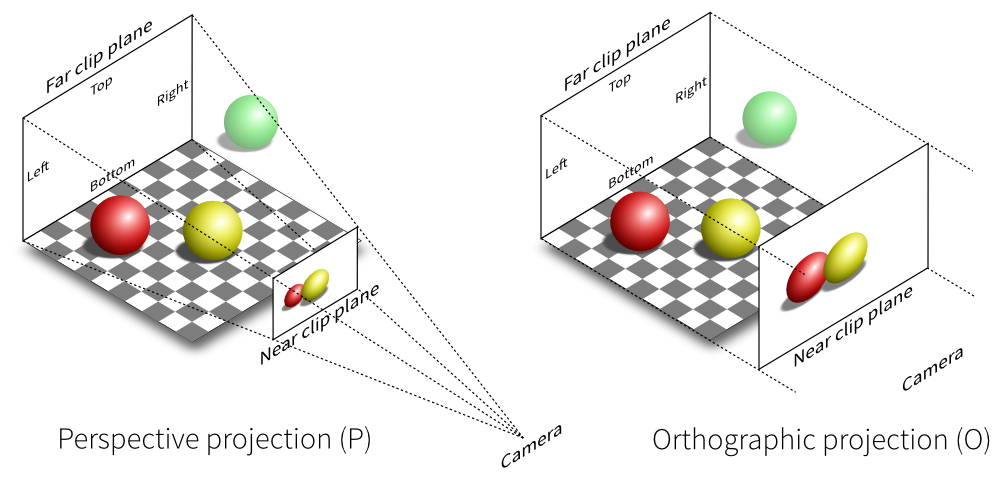
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int delta1[4][2] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 1};
const int delta2[8][2] = {-2, -1, -2, 1, -1, -2, -1, 2, 1, -2, 1, 2, 2, -1, 2, 1};
const int MAXI = 90;
const int MAXJ = 9;
const int MAXK = 9;
struct Node {
int degree;
bool flag;
int step;
vector<Node *> edge;
inline void addEdge(Node *x) {
degree++;
x->edge.push_back(this);
}
} nodes[MAXI + 1][MAXJ][MAXK][2];
inline bool valid(const int x, const int y) {
return x >= 0 && x <= 9 && y >= 0 && y <= 8;
}
inline bool equals(const int x1, const int y1, const int x2, const int y2) {
return x1 == x2 && y1 == y2;
}
inline void init() {
for (register int i = 0; i <= MAXI; i++) {
for (register int j = 0; j < MAXJ; j++) {
for (register int k = 0; k < MAXK; k++) {
Node *cur1 = &nodes[i][j][k][0], *cur2 = &nodes[i][j][k][1];
register int xi = i / MAXJ, yi = i % MAXJ, xj = j / 3 + 7, yj = j % 3 + 3, xk = k / 3, yk = k % 3 + 3;
if (equals(xi, yi, xj, yj) || equals(xi, yi, xk, yk))
continue;
if (i != MAXI) {
for (register int d = 0; d < 8; d++) {
register int xi1 = xi + delta2[d][0], yi1 = yi + delta2[d][1];
if (equals(xi1, yi1, xk, yk)) {
cur1->flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (yj == yk && (yi != yj || xi < xk || xi > xj))
cur1->flag = true;
if (!cur1->flag) {
if (i != MAXI) {
for (register int d = 0; d < 8; d++) {
register int xi1 = xi + delta2[d][0], yi1 = yi + delta2[d][1];
int tmp[2] = {xi + delta2[d][0] / 2, yi + delta2[d][1] / 2};
if (valid(xi1, yi1) && !equals(xi1, yi1, xj, yj) && !equals(tmp[0], tmp[1], xj, yj) && !equals(tmp[0], tmp[1], xk, yk))
cur1->addEdge(&nodes[xi1 * 9 + yi1][j][k][1]);
}
}
for (register int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
register int xj1 = xj + delta1[d][0], yj1 = yj + delta1[d][1];
if (xj1 >= 7 && xj1 <= 9 && yj1 >= 3 && yj1 <= 5 && !equals(xj1, yj1, xi, yi))
cur1->addEdge(&nodes[i][(xj1 - 7) * 3 + (yj1 - 3)][k][1]);
}
}
if (yj == yk && (yi != yj || xi < xk || xi > xj))
cur2->flag = true;
if (!cur2->flag) {
for (register int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
register int xk1 = xk + delta1[d][0], yk1 = yk + delta1[d][1];
if (xk1 >= 0 && xk1 <= 2 && yk1 >= 3 && yk1 <= 5)
cur2->addEdge(&nodes[equals(xk1, yk1, xi, yi) ? 90 : i][j][xk1 * 3 + yk1 - 3][0]);
}
}
}
}
}
queue<Node *> q;
for (register int i = 0; i <= MAXI; i++) {
for (register int j = 0; j < MAXJ; j++) {
for (register int k = 0; k < MAXK; k++) {
for (register int l = 0; l <= 1; l++) {
Node *x = &nodes[i][j][k][l];
if (x->flag) {
x->step = 1;
q.push(x);
}
}
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *v = q.front();
q.pop();
if (v->flag) {
for (vector<Node *>::iterator it = v->edge.begin(); it != v->edge.end(); it++) {
Node *u = *it;
if (u->step) continue;
if(!--u->degree) {
u->flag = false;
u->step = v->step + 1;
q.push(u);
}
}
} else {
for (vector<Node *>::iterator it = v->edge.begin(); it != v->edge.end(); it++) {
Node *u = *it;
if (u->step) continue;
u->flag = true;
u->step = v->step + 1;
q.push(u);
}
}
}
}
inline void solve() {
int x1, x2, x3, y1, y2, y3, l;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> x3 >> y3 >> l;
register int i = x1 * 9 + y1, j = (x2 - 7) * 3 + (y2 - 3), k = x3 * 3 + (y3 - 3);
Node *cur = &nodes[i][j][k][l ^ 1];
if (!l) {
if (!cur->step)
cout << "Lucky guy!\n";
else if (cur->flag)
cout << "Lucky guy!\n";
else cout << "Lose in " << cur->step << " steps T.T!\n";
} else {
if (!cur->step)
cout << "Lucky guy!\n";
else if (cur->flag)
cout << "Lose in " << cur->step << " steps T.T!\n";
else cout << "Lucky guy!\n";
}
}
int main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
init();
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
|